Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Mov Disord > Volume 2(1); 2009 > Article
-
Case Report
Parkinsonsim due to a Chronic Subdural Hematoma - Bosuk Park, Sook Keun Song, Jin Yong Hong, Phil Hyu Lee
-
Journal of Movement Disorders 2009;2(1):43-44.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.09011
Published online: April 30, 2009
Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Phil Hyu Lee, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 250 Seongsan-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-752, Korea, Tel +82-2-2228-1608, Fax +82-2-393-0705, E-mail phisland@chol.net
• Received: March 4, 2009 • Revised: March 21, 2009 • Accepted: March 11, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Movement Disorder Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 11,827 Views
- 81 Download
- 4 Crossref
ABSTRACT
- Subdural hematoma is a rare cause of parkinsonism. We present the case of a 78-year-old man with right-side dominant parkinsonism about 3 months after a minor head injury. MRI reveals a chronic subdural hematoma on the left side with mildly displaced midline structures. The parkinsonian features were almost completely disappeared after neurosurgical evacuation of the hematoma without any anti-parkinson drug.
- A 78-year-old man noted dysarthria, gait slowness, and clumsiness when using spoon and chopsticks with his right hand for 2 weeks. He had a history of hypertension and experienceed head trauma due to falling down from the bed without altered consciousness about 3 months ago. The patient denied history of any anti-dopaminergic drugs.
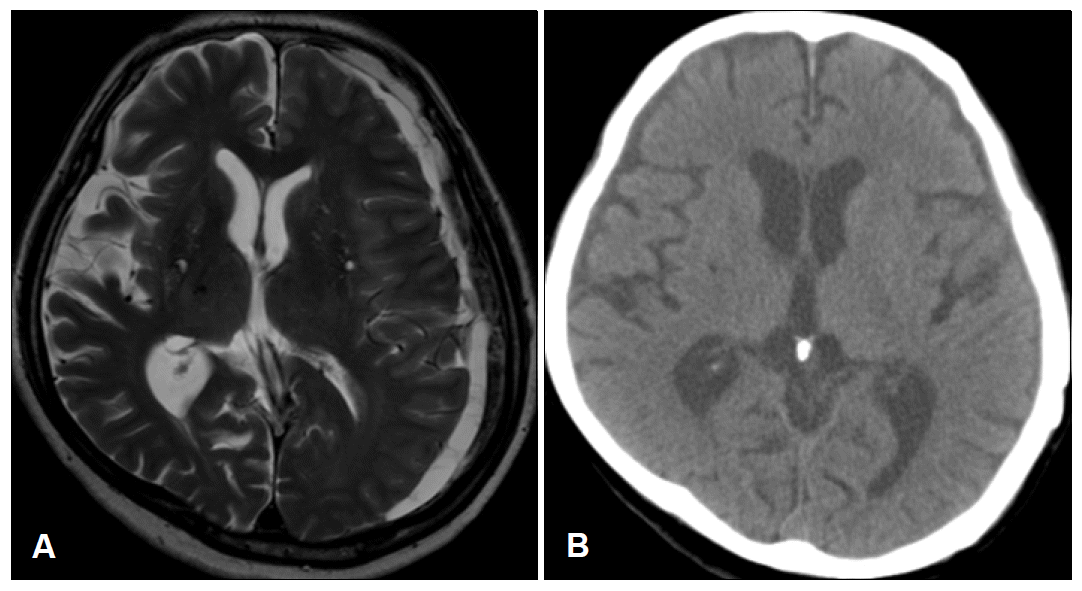
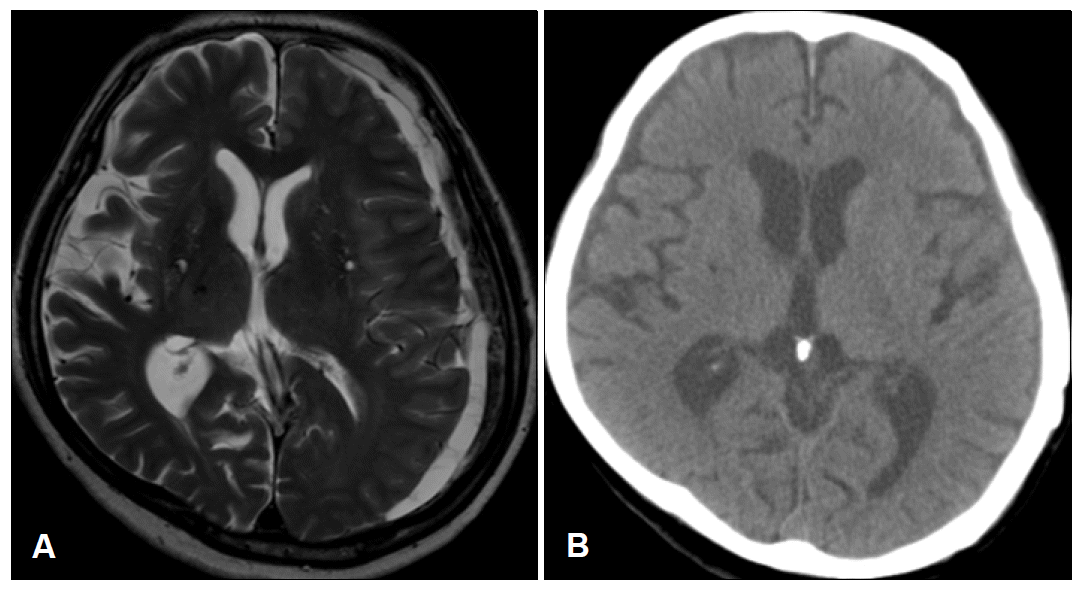
- On neurologic examination, mental status was alert and orientation for time and place was impaired. Dyscalculia and impairment in memory registration were noted. Naming, reading, writing and repetition were normal. There were mild hypomimia and rigidity on right extremity. The speed of finger and foot tapping was mildly decreased on right extremities. On gait, there was decreased arm swing on right side with normal base and preserved gait velocity. Neither tremor nor postural instability was shown. There was a slight weakness on right arm showing pronator drift on arm stretching. No other pyramidal sign was checked. Sensory examination was normal. The Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor score was 27. Brain MRI showed a chronic subdural hematoma in the left convexity with slight midline shift to right (Figure 1A). The hematoma was evacuated by means of burr hole drainage on the next day. After 3 weeks, the rigidity, bradykinesia and gait slowness had almost completely disappeared (UPDRS motor score of 8). The olfactory identification function was normal (Cross-Cultural Smell Identification Test: 9/ in a total of 12). The follow-up brain CT showed no remnant hematoma (Figure 1B).
Case Report
- Several cases of parkinsonism related subdural hematomas have been reported. Most were elderly patients with CSH, who subacutely developed parkinsonism. Surgical evacuation2–4 or spontaneous resolution5 of the hematomas induced partial or complete recovery from the parkinsonism. Another case with dopa-responsive parkinsonism after subdural hematoma also have been reported.6 In the latter case, parkinsonian features occurred after surgical treatment of the subdural hematoma. Interestingly, the parkinsonian features occurred ipsilesional side of the subdural hematomas and nigral dopaminergic density using (123I) beta-CIT SPECT scan (DAT scan)6 and [18F] dopa positron-emission tomography7 were markedly decreased on the contralesional striatum of the hematoma, suggesting contralateral nigrostriatal lesion caused by midline shift.
- The mechanism leading to parkinsonism in patients with a subdural hematoma is not well understood. It has been suggested that direct compression on the basal ganglia by space-occupying lesions can cause the decreased number of dopaminergic receptors in the striatum which explains parkinsonism secondary to brain tumor.8 Furthermore, the mass effect that compress the midbrain and thus interfere nigro-striatal dopaminergic transmission may also induce parkinsonism. In those mechanism, the levodopa-responsiveness may be depending on the region of compression and the involvement in the midbrain tend to be more responsive rather than basal ganglia compression.9 Alternatively, with a viewpoint that secondary parkinsonisms related with space-occupying lesions are more prevalent in old age, it is possible that space-occupying lesions may unmask underlying subclinical status of Parkinson’s disease in a similar fashion that anti-dopaminergic drugs may unmask preclinical Parkinson’s disease.10 In that smell identification was well preserved in our patient, it is less likely that subdural hematoma may exaggerate preclinical status of PD in our patient.
- Although parkinsonism secondary to CSH is rare etiology, it is important to recognize because it is potentially treatable. With careful history taking, it is recommended to take a brain imaging in patients with parkinsonism, especially showing acute or subacute onset.
Discussion
Figure 1.A: Brain MRI shows a chronic subdural hematoma in the left convexity with slight midline shift to right. B: The postop brain CT taken at 3 weeks later shows no remnant hem-atoma.

- 1. Quinn N. Parkinsonism--recognition and differential diagnosis. BMJ 1995;310:447–452.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Sunada I, Inoue T, Tamura K, Akano Y, Fu Y. Parkinsonism due to chronic subdural hematoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1996;36:99–101.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Suman S, Meenakshisundaram S, Woodhouse P. Bilateral chronic subdural haematoma: a reversible cause of parkinsonism. J R Soc Med 2006;99:91–92.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Bostantjopoulou S, Katsarou Z, Michael M, Petridis A. Reversible parkinsonism due to chronic bilateral subdural hematomas. J Clin Neurosci 2009;16:458–460.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Hageman AT, Horstink MW. Parkinsonism due to a subdural hematoma. Mov Disord 1994;9:107–108.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Maertens de Noordhout A, Daenen F, Bex V. Dopa-responsive parkinsonism after acute subdural hematoma. Eur J Neurol 2006;13:e10–11.Article
- 7. Turjanski N, Pentland B, Lees AJ, Brooks DJ. Parkinsonism associated with acute intracranial hematomas: an [18f]dopa positron-emission tomography study. Mov Disord 1997;12:1035–1038.ArticlePubMed
- 8. García de Y’ebenes J, Gervas JJ, Iglesias J, Mena MA, Martín del Rio R, Somoza E. Biochemical findings in a case of parkinsonism secondary to brain tumor. Ann Neurol 1982;11:313–316.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Ling MJ, Aggarwal A, Morris JG. Dopa-responsive parkinsonism secondary to right temporal lobe haemorrahage. Mov Disord 2002;17:402–404.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Lee PH, Yeo SH, Yong SW, Kim YJ. Odour identification test and its relation to cardiac 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine in patients with drug induced parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2007;78:1250–1252.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Systematic Review of Post-Traumatic Parkinsonism, an Emerging Parkinsonian Disorder Among Survivors of Traumatic Brain Injury
Catherine Rojvirat, Gabriel R. Arismendi, Erin Feinstein, Maynard Guzman, Bruce A. Citron, Vedad Delic
Neurotrauma Reports.2024; 5(1): 37. CrossRef - Parkinsonism-like features following reconstructive cranioplasty
Mayank Tyagi, Charu Mahajan, Indu Kapoor, Hemanshu Prabhakar
Neurological Sciences.2021; 42(4): 1591. CrossRef - Chronic subdural hematoma-induced parkinsonism: A systematic review
Achmad Fahmi, Heru Kustono, Komang Sena Adhistira, Heri Subianto, Budi Utomo, Agus Turchan
Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery.2021; 208: 106826. CrossRef - Secondary parkinsonism caused by chronic subdural hematomas owing to compressed cortex and a disturbed cortico–basal ganglia–thalamocortical circuit: illustrative case
Masao Fukumura, Sho Murase, Yuzo Kuroda, Kazutomo Nakazawa, Yasufumi Gon
Journal of Neurosurgery: Case Lessons.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
Comments on this article
 KMDS
KMDS
 E-submission
E-submission
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite