Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Mov Disord > Volume 9(2); 2016 > Article
-
Review Article
Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation for Treatment of Focal Hand Dystonia: Update and Future Direction - Hyun Joo Cho, Mark Hallett
-
Journal of Movement Disorders 2016;9(2):55-62.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.16014
Published online: May 25, 2016
Human Motor Control Section, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA
- Corresponding author: Mark Hallett, MD, Human Motor Control Section, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, 10 Center Drive MSC 1428, Building 10, Room 7D37, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA Tel: +1-301-496-9526 Fax: +1-301-480-2286 E-mail: hallettm@ninds.nih.gov
Copyright © 2016 The Korean Movement Disorder Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- Focal hand dystonia (FHD) is characterized by excessive and unwanted muscle activation in both the hand and arm resulting in impaired performance in particular tasks. Understanding the pathophysiology of FHD has progressed significantly for several decades and this has led to consideration of other potential therapies such as non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS). A number of studies have been conducted to develop new therapy for FHD using transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation. In this paper, we review previous studies and describe the potential therapeutic use of NIBS for FHD. We also discuss the future direction of NIBS to treat FHD.
- Focal hand dystonia (FHD) is characterized by excessive and unwanted muscle activation in both the hand and arm resulting in impaired performance in particular tasks. Writer’s cramp (WC) and musician’s dystonia (MD) are the most common forms of FHD, but numerous other occupational FHD have been identified [1]. FHD generally occurs in people who have spent a long period of time performing repetitive skilled fine motor tasks. Botulinum toxin is usually the most effective treatment [2] for FHD whereas oral medications are often limited in efficacy and cause side effects. However, FHD has a lower overall response rate to botulinum toxin, with about 50% of WC patients receiving at least mild benefit compared to 80% for cervical dystonia and over 90% for blepharospasm [3]. This may be due to complex patterns of the hand movements, numbers of muscles involved, and challenges in discriminating primary abnormal movements from compensatory movements. Clearly, new therapeutic measures are needed for FHD patients.
- Understanding the pathophysiology of FHD has progressed significantly for several decades and this has led to consideration of other potential therapies such as non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS). There are several general abnormalities that appear to play a role in the pathophysiology of dystonia including loss of inhibition, sensory dysfunction, and abnormal plasticity [4]. FHD is thought to be a network disorder involving large areas of the brain, not confined to the striatum. Many studies demonstrated increased excitability or loss of inhibition at multiple levels including motor cortex (M1), premotor cortex (PMC), somatosensory cortex (S1), and cerebellum [5-8]. Hence, a reasonable aim of treatment is to reverse these pathological abnormalities in the aforementioned areas of the brain to restore normal physiology associated with improved behavior. With this idea, a number of studies have been conducted to develop new therapy for FHD using repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS).
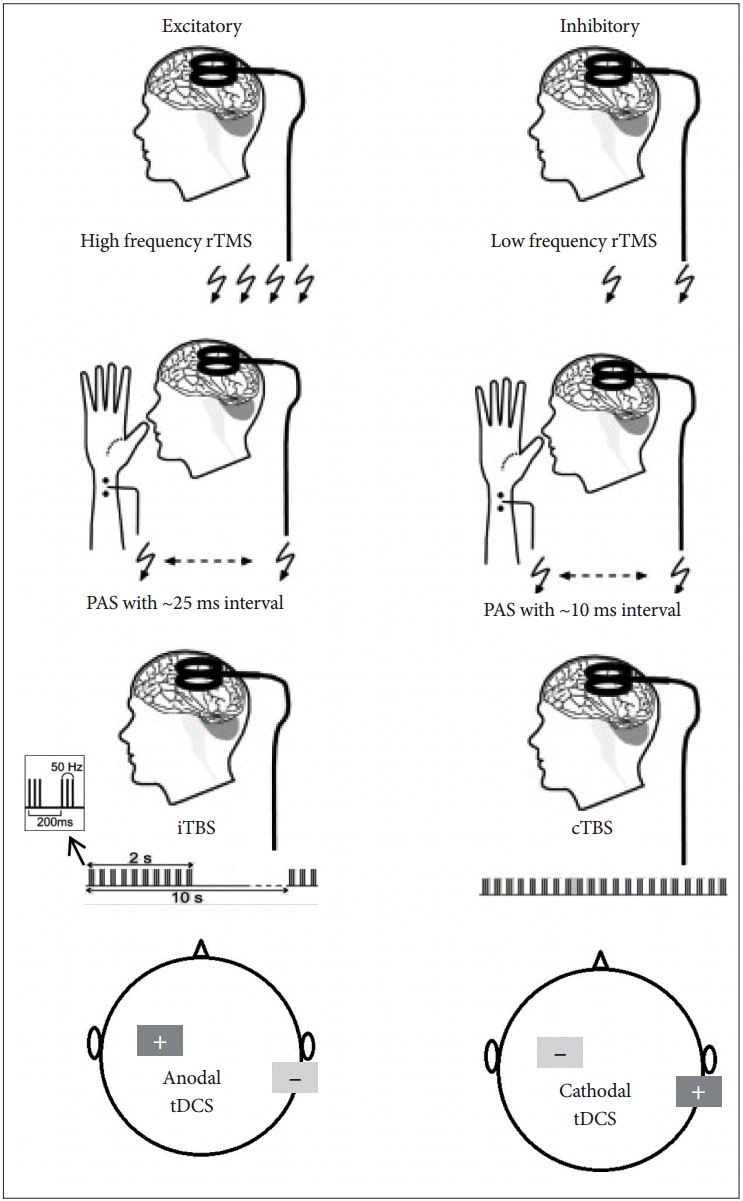
- NIBS can induce plastic changes in the brain in a variety of ways (Figure 1). Current rTMS protocols apply low- (< 1 Hz) or high-frequency (≥ 5 Hz) stimulation. Generally, high-frequency stimulation induces increased cortical excitability [9] and low-frequency stimulation decreases cortical excitability [10]. M1 plasticity can be also induced by paired associative stimulation (PAS) which employs repetitive pairs of TMS over M1 and peripheral nerve stimulation. Amplitude of motor-evoked potential (MEP) can be facilitated by using interval of ~25 ms (PAS 25) between the nerve stimulation and the TMS and MEP amplitude is inhibited by using interval of ~10 ms (PAS 10). This plastic facilitation and inhibition resembles characteristics of long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression [11]. An alternative method of rTMS is theta burst stimulation (TBS), consisting of short, repeated bursts of TMS pulses at high frequency [12]. A typical paradigm would be a burst of three stimuli at 50 Hz with the burst repeated at 5 Hz. Continuous TBS decreases excitability while intermittent TBS increases excitability. As for tDCS, anodal stimulation is known to increase excitability of the stimulated area whereas cathodal stimulation decreases excitability [13]. These modalities were applied to various brain targets that are thought to be involved in pathophysiology of FHD. In recent years, rTMS and tDCS have received significant attention as potential new therapeutic measures because of their safety and potential efficacy [14].
- In this paper, we will review previous studies and describe the potential therapeutic use of NIBS for FHD. We will also discuss the future direction of NIBS to treat FHD.
INTRODUCTION
- Fourteen articles were selected from those identified by a Pubmed search using the keywords ‘focal hand dystonia’, ‘writer’s cramp’, ‘musician’s dystonia’, ‘noninvasive brain stimulation’, ‘transcranial magnetic stimulation’, and ‘transcranial direct current stimulation’. Studies that measured clinical outcome were chosen for this review article. Seven studies performed rTMS (Table 1) and seven studies applied tDCS (Table 2) for therapeutic use in FHD.
NIBS TO TREAT FHD
- Among seven rTMS studies, five studied WC patients and three had a mixed group of patients with MD and WC (Table 1). Various study designs were used, either single- or double-blinded mostly with sham control, crossover or parallel randomization. Crossover design seems to have been used most frequently, likely due to small sample size. In terms of the intervention, all studies used low-frequency subthreshold rTMS to enhance cortical inhibition. Early studies used single-session inhibitory rTMS and measured the outcome right after the intervention for proof of concept [15,16]. More recent studies applied prolonged sessions for 5 consecutive days or longer and assessed the outcome at more than one time point [17-21]. Although small effects of a single session were reported, repetitive sessions over consecutive days seem to be required for clearer therapeutic effects.
- Different brain areas were used as a target of stimulation including M1, PMC, and S1, on the contralateral side to dystonia. The first study done by Siebner et al. [16] showed that inhibitory rTMS on M1 might have potential benefit, but Murase et al. [15] showed that PMC was a better target when compared with M1 and supplementary motor area (SMA). Subsequently, four more studies used PMC as the target [17,19-21] and all studies showed promising results either by physiologic or behavioral measures or both. Kimberley et al. [21] studied whether sensorimotor retraining in addition to rTMS on PMC would add further benefit, but failed to prove any additional benefit from sensorimotor retraining. One study targeting S1 showed improved writing associated with rTMS-induced blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) signal increase bilaterally in the SI cortex, posterior parietal cortex, and the SMA [18].
- Why does it work?
- To determine outcome, some studies also measured changes of physiological markers in neurophysiology or neuroimaging in addition to a subjective and/or objective writing assessment. This might help demonstrate why rTMS would work if it did. The pathological hallmark of FHD is increased cortical excitability that can be demonstrated as reduced intracortical inhibition [5] and a cortical silent period [22]. Several studies showed reversal of this abnormal physiology by applying low-frequency rTMS [15-17,19,20]. Havrankova et al. [18] examined changes in functional magnetic resonance imaging in ‘responders’ to an rTMS protocol and found bilateral BOLD signal increase in the posterior parietal cortex, SMA, and right anterior insula. In one positron emission tomography study, there was a greater decrease of regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) in lateral and medial premotor areas, putamen, and thalamus, including the stimulated PMC, and a larger increase in cerebellar rCBF after one session of premotor rTMS in FHD patients compared to healthy controls [23]. These imaging studies prove that rTMS affects regional synaptic activity in widespread areas of the motor system, but it is not clear how they explain the therapeutic effect.
- What are the limitations?
- Most studies adapted a crossover design with randomization because of small patient sample size. However, it may not be the best study design due to the potential carry-over effect of rTMS. Most studies used a 1-week interval except Havrankova et al. [18] who used 4–10 weeks; however, 1 week might not enough time for washout since some studies showed [18,21] that more than one week was necessary to be effective. In Kimberley’s study, patients did not return to their baseline even with a one-month washout period, which likely blurred the accurate outcome measure [21]. Also, there are many methodological variations across the studies in terms of rTMS protocol. Accurate positioning of the coil on the brain target could be critical [18] and different studies adopted different ways for the same target. For example, 2.5 cm anterior to the first dorsal interosseous (FDI) hot spot was set for PMC target in one study [19], whereas 1 cm medial and 2 cm rostral to the FDI hotspot was used in another study [20]. There are also variations in intensity (85–90% active motor threshold vs. 90% resting motor threshold), frequency (0.2 Hz or 1 Hz), and type of TMS (monophasic vs. biphasic). This variability makes it difficult to compare results across studies, but can be important for the future development of optimal treatment parameters.
- In summary, PMC seems to be a promising target for a treatment protocol of rTMS and prolonged sessions may result in better clinical outcomes. However, it is still unclear how long rTMS treatment is needed to sustain significant clinical benefit and how long the benefit might last. There are less data for MD than for WC. Dedicated rTMS for MD might be necessary to refine a treatment protocol.
rTMS STUDIES FOR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSE
- Of the seven tDCS studies, two were performed for WC, four for MD and two were mixed. Again, various study designs were used either with single or prolonged sessions. Four studies applied tDCS on M1, and three showed no clinical benefit when stimulating the affected M1 with cathodal tDCS [24-26]. However, when cathodal tDCS on the affected M1 was combined with anodal tDCS on unaffected M1 in MD pianists, rhythmic accuracy of sequential finger movements was improved [27]. In the same study, the authors also tested whether tDCS during rest vs. motor training would be different; indeed, it was only effective when tDCS was applied combined with motor training. The cerebellum was the target location in two studies [28,29] and the results were contradictory. The idea behind anodal tDCS on the cerebellum was to enhance cerebellar activity and modulate M1 plasticity which is abnormally increased in FHD patients. The study done by Sadnicka et al. [29] for WC patients could not demonstrate any changes in clinical symptoms and also failed to show changes in M1 plasticity to PAS 25. However, it was noted that PAS 25 response varied considerably among patients. Some patients had facilitatation with PAS 25 as expected and others had inhibition to the same protocol. Interestingly, cerebellar tDCS reduced M1 plasticity only in ‘facilitators’ but not in ‘inhibitors’. Another study showed that anodal tDCS on cerebellum in WC patients improved writing kinematics and reduced cerebellar inhibition (CBI), but clinical improvement was not correlated with changes in CBI [28]. Most recently, the largest double-blind controlled study done in 30 MD patients showed that bilateral parietal tDCS might hold potential therapeutic benefits [30].
- Why does it work?
- Only a few tDCS studies tried to address the underlying mechanism of either the tDCS effect or its absence [24,28,29]. None of the studies showed changes in neurophysiology or neuroimaging that might be correlated with clinical benefit. Two studies examined neurophysiology, but there was neither clinical benefit nor positive changes in physiology. One study [28] showed reduced CBI after anodal tDCS but this was not correlated with symptom improvement; therefore, this is likely not the underlying mechanism for clinical benefit. Further studies are required to elucidate the mechanism of tDCS effects in treating dystonia by combining tDCS with functional imaging or neurophysiology techniques such as electroencephalogram or TMS.
- What are the limitations?
- Most tDCS studies adopted prolonged sessions, 1 or 2 weeks, with or without concomitant sensorimotor training. However, the duration of prolonged treatment sessions was not well studied. Furuya et al. [27] reported that the effect was retained 4 days after the intervention, but it is not clear whether the effect might have lasted longer. This is important to know in order to properly design future clinical trials. tDCS is known to cause lasting effects (up to 5 hr) from a single session if the stimulation is sufficiently long (10–30 min) [13]. The duration of the prolonged session needs to be studied. Also, there are many variations in experimental details as to how exactly tDCS was applied. Most of the studies used a 10–20 system to localize C3 and C4 as targets [25-27,30], but one study used the first dorsal FDI hotspot as the target [24]. It is clear that placement of the reference is very important to shape the electric flow [31] and it may change the behavioral outcome as well. For an outcome measure, it is particularly difficult for MD to have a single uniform dystonia scale due to variable instruments and different skills. This issue needs to be addressed by experts in this area.
- In summary, bi-hemispheric tDCS on sensorimotor cortices with cathodal tDCS on the affected hemisphere together with anodal tDCS on the unaffected hemisphere combined with sensorimotor retraining seem to be promising for therapeutic purposes. Further studies are required to elucidate the mechanism of the tDCS effect in treating dystonia using multimodal experiments.
tDCS STUDIES FOR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSE
- While NIBS for treating dystonia seems to be promising, there are many unanswered questions that can be addressed in future studies. First, we need a properly designed large, multi-center, randomized controlled trial with longer duration of rTMS intervention to provide a greater opportunity for cumulative therapeutic and adverse effects to be expressed. In rTMS trials for depression, 3–6 weeks duration has been typical [32] and the effect seemed to last for 1 year based on the follow-up study [33]. FHD generally takes years of repetitive tasks to become apparent, and it is possible that it may take a long time to reverse the disordered motor program as seen in cases of deep brain stimulation [34]. Second, characterization of “responders” and “non-responders” would be useful to predict the response to NIBS intervention. Demographics, for example, age or disease duration might affect the responsiveness to NIBS. In fact, one study reported that age might be a predictor for a response to rTMS intervention [20]. Baseline neurophysiology might serve as an indicator of responsiveness. One study showed that patients who had LTP-like response to PAS 25 interval showed changes in M1 plasticity after cerebellar tDCS, but others who did not show LTP-like response elicited no changes in M1 plasticity with the same intervention [29]. Kimberley et al. [35] demonstrated in a small sample (n = 2) study that the individual with baseline TMS responses indicating impaired inhibition responded favorably to the rTMS intervention. These results point out that not everyone might have a desirable outcome from NIBS, and a more individualistic approach is required to determine therapeutic options. But, first, we need to study who might benefit from NIBS. Last, the benefit of combined neurorehabilitation with NIBS should be studied in more detail. Previous studies used NIBS with sensorimotor training under the assumption that neurorehabilitation with a sensorimotor retraining program could induce a synergistic benefit when given with NIBS [36], but, to date, the results are mixed. It is necessary to explore an additive or synergistic effect of sensorimotor training program with the potential to transform clinical practice.
FUTURE DIRECTION
- Although they were not reviewed in this paper, there are other methods of non-invasive neuromodulation that have been tried in FHD other than rTMS or tDCS. Proprioceptive training using vibration was studied in MD patients, and it was shown to effectively restore sensorimotor organization [37]. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation over forearm flexor muscles was tried in WC, and it decreased MEP amplitude in the flexor carpi radialis and increased it in the extensor carpi radialis which was paralleled by improved handwriting [38]. Neurofeedback, using a brain-computer interface, is another method that has received attention for non-invasive neuromodulation. A preliminary study with two WC patients showed impressive results in one of them [39]. There may be more such studies in the future.
OTHER NON-INVASIVE NEUROMODULATION
- rTMS and tDCS can be powerful tools to better understand and treat FHD. Clear consensus on optimal protocols needs to be established, and multicenter randomized clinical trials with large numbers of patients are required to implement the technique in clinical practice.
CONCLUSION
- Dr. Cho has received a research grant from the Dystonia Medical Research Foundation. Dr. Hallett serves as Chair of the Medical Advisory Board for and receives honoraria and funding for travel from the Neurotoxin Institute. He may accrue revenue on US Patent #6 780 413 B2 (Issued: 24 August 2004): Immunotoxin (MAB-Ricin) for the treatment of focal movement disorders, and US Patent #7 407 478 (Issued: 5 August 2008): Coil for Magnetic Stimulation and methods for using the same (H-coil); in relation to the latter, he has received license fee payments from the National Institutes of Health (NIH; from Brainsway) for licensing of this patent. He is on the editorial board of 20 journals and received royalties and/or honoraria from publishing from Cambridge University Press, Oxford University Press, John Wiley & Sons, Wolters Kluwer, Springer, and Elsevier. He has received honoraria for lecturing from Columbia University. Dr. Hallett’s research at the NIH is largely supported by the NIH Intramural Program. Supplemental research funds have been granted by the Kinetics Foundation for studies of instrumental methods to monitor Parkinson’s disease, BCN Peptides, S.A. for treatment studies of blepharospasm, Medtronics, Inc., for studies of DBS, Parkinson Alliance for studies of eye movements in Parkinson’s disease, Merz for treatment studies of focal hand dystonia, and Allergan for studies of methods to inject botulinum toxins.
- We thank Ms. Devee Schoenberg for skillful editing.
Acknowledgments
| References | Patient group | Study design | Intervention | Target of the stimulation | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siebner et al. [16] | 16 WC patients and 11 HV | Open-label | Single session of 1 Hz rTMS at 10% below the RMT (1,800 biphasic stimuli) | Left M1 | Significantly reduced mean writing pressure, normalization of the deficient cortico-cortical inhibition, and prolongation of the cSP |
| Murase et al. [15] | 9 WC and 7 HV | Single-blinded | Single session of 0.2 Hz rTMS at 85% RMT (250 monophasic stimuli) vs. sham | M1, PMC, and SMA | Decreased tracking error and pen pressure with PMC stimulation, prolongation of cSP with PMC stimulation |
| Borich et al. [17] | 6 FHD (3 WC and 3 MD) and 9 HV | Single-blinded partial cross-over | 1 Hz rTMS at 90% RMT (900 monophasic stimuli) vs. sham for 5 days | PMC | Improved handwriting performance and reduced cortical excitability 10 days post treatment |
| Havrankova et al. [18] | 11 WC | Double-blinded cross-over | 1 Hz at 90% AMT (biphasic 1,800 stimuli) vs. sham-rTMS for 5 days | SI contralateral to affected hand | Subjective and objective improvement in writing 2 weeks post treatment associated with increased task-related BOLD in fMRI |
| Huang et al. [19] | 18 WC and 8 HV | Single-blinded randomized parallel | cTBS (3-pulse 50 Hz burst every 200 ms at 80% AMT for 40 sec) vs. sham daily for 5 days | Left PMC | More subjective improvement in writing with real rTMS Restoration of SICI, PMC-M1 interaction, and reduced M1 plasticity |
| Kimberley et al. [20] | 12 FHD | Single-blinded randomized with partial cross-over | 1 Hz rTMS with 90% RMT (biphasic 1,800 stimuli) vs. sham during non-dystonic writing movement for 5 days | Contralateral PMC | Prolonged cSP and reduced pen force |
| Kimberley et al. [21] | 9 FHD | Randomized with cross-over | 5 days 1 Hz rTMS at 80% RMT (biphasic 1,200 pulses) + sensorimotor retraining vs. rTMS + control therapy | PMC | No additional benefit from sensorimotor retraining |
rTMS: repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, WC: writer’s cramp, HV: healthy volunteer, RMT: resting motor threshold, cSP: cortical silent period, PMC: premotor cortex, SMA: supplementary motor area, FHD: focal hand dystonia, MD: musician’s dystonia, AMT: active motor threshold, BOLD: blood oxygenation level dependent, fMRI: functional magnetic resonance imaging, cTBS: continuous theta burst stimulation, SICI: short latency intracortical inhibition, M1: motor cortex.
| References | Patient group | Study design | Intervention | Target of the stimulation | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buttkus et al. [26] | 10 MD (guitarists) | Double-blinded randomized with cross-over | Single session of cathodal tDCS (2 mA for 20 min) vs. placebo | Left M1 | No change in fine motor control after 30 min |
| Benninger et al. [24] | 12 WC | Double-blinded randomized, sham-controlled with parallel | Prolonged sessions (3 in 1 week) of cathodal tDCS | M1 contralateral to FHD | No positive effects in clinical measures nor handwriting and cortical excitability |
| Buttkus et al. [25] | 9 MD (pianists) | Double-blinded sham-controlled with cross-over | Anodal tDCS, cathodal tDCS (2 mA for 20 min) during sensorimotor retraining | Left M1 | No favorable result in behavior |
| Furuya et al. [27] | 10 MD, 10 healthy musicians (pianists) | Double-blinded sham-controlled with cross-over | tDCS (2 mA for 24 min) during bimanual mirrored finger movements | Bihemispheric motor cortices | Improved rhythmic accuracy of sequential finger movements with cathodal-affected and anodal-unaffected tDCS |
| Sadnicka et al. [29] | 10 WC | Single-blinded sham-controlled with cross-over | Single session anodal tDCS (sham-controlled) | Cerebellum | No changes in clinical symptoms nor in M1 plasticity |
| Bradnam et al. [28] | 8 FHD (5 WC, 3 MD) and 8 HV | Double-blinded randomized sham-controlled with cross-over | Anodal, cathodal (2 mA, 20 min) or sham tDCS | Cerebellum | Improved writing kinematics and decreased CBI with anodal tDCS |
| Rosset-Llobet et al. [30] | 30 MD | Parallel double-blind randomized design | tDCS (real vs. sham) for 30 min coupled with 1 hr sensory motor retuning therapy for 2 weeks (10 days) | Cathode over left and anode over right parietal regions | Improved dystonia severity score in both groups; more benefit in real tDCS than sham group |
- 1. Hunter D. The diseases of occupations. 6th ed. London: Hodder and Stoughton; 1978.
- 2. Lungu C, Ahmad OF. Update on the use of botulinum toxin therapy for focal and task-specific dystonias. Semin Neurol 2016;36:41–46.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Lungu C, Karp BI, Alter K, Zolbrod R, Hallett M. Long-term follow-up of botulinum toxin therapy for focal hand dystonia: outcome at 10 years or more. Mov Disord 2011;26:750–753.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Quartarone A, Hallett M. Emerging concepts in the physiological basis of dystonia. Mov Disord 2013;28:958–967.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Beck S, Richardson SP, Shamim EA, Dang N, Schubert M, Hallett M. Short intracortical and surround inhibition are selectively reduced during movement initiation in focal hand dystonia. J Neurosci 2008;28:10363–10369.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Brighina F, Romano M, Giglia G, Saia V, Puma A, Giglia F, et al. Effects of cerebellar TMS on motor cortex of patients with focal dystonia: a preliminary report. Exp Brain Res 2009;192:651–656.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Delnooz CC, Helmich RC, Medendorp WP, Van de Warrenburg BP, Toni I. Writer’s cramp: increased dorsal premotor activity during intended writing. Hum Brain Mapp 2013;34:613–625.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Tamura Y, Matsuhashi M, Lin P, Ou B, Vorbach S, Kakigi R, et al. Impaired intracortical inhibition in the primary somatosensory cortex in focal hand dystonia. Mov Disord 2008;23:558–565.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Pascual-Leone A, Valls-Solé J, Wassermann EM, Hallett M. Responses to rapid-rate transcranial magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex. Brain 1994;117(Pt 4):847–858.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 10. Chen R, Classen J, Gerloff C, Celnik P, Wassermann EM, Hallett M, et al. Depression of motor cortex excitability by low-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 1997;48:1398–1403.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Stefan K, Kunesch E, Cohen LG, Benecke R, Classen J. Induction of plasticity in the human motor cortex by paired associative stimulation. Brain 2000;123 Pt 3:572–584.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Huang YZ, Edwards MJ, Rounis E, Bhatia KP, Rothwell JC. Theta burst stimulation of the human motor cortex. Neuron 2005;45:201–206.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Nitsche MA, Paulus W. Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J Physiol 2000;527 Pt 3:633–639.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Edwards MJ, Talelli P, Rothwell JC. Clinical applications of transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with movement disorders. Lancet Neurol 2008;7:827–840.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Murase N, Rothwell JC, Kaji R, Urushihara R, Nakamura K, Murayama N, et al. Subthreshold low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the premotor cortex modulates writer’s cramp. Brain 2005;128(Pt 1):104–115.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Siebner HR, Tormos JM, Ceballos-Baumann AO, Auer C, Catala MD, Conrad B, et al. Low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex in writer’s cramp. Neurology 1999;52:529–537.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Borich M, Arora S, Kimberley TJ. Lasting effects of repeated rTMS application in focal hand dystonia. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2009;27:55–65.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Havrankova P, Jech R, Walker ND, Operto G, Tauchmanova J, Vymazal J, et al. Repetitive TMS of the somatosensory cortex improves writer’s cramp and enhances cortical activity. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2010;31:73–86.
- 19. Huang YZ, Lu CS, Rothwell JC, Lo CC, Chuang WL, Weng YH, et al. Modulation of the disturbed motor network in dystonia by multisession suppression of premotor cortex. PLoS One 2012;7:e47574. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Kimberley TJ, Borich MR, Arora S, Siebner HR. Multiple sessions of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in focal hand dystonia: clinical and physiological effects. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2013;31:533–542.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Kimberley TJ, Schmidt RL, Chen M, Dykstra DD, Buetefisch CM. Mixed effectiveness of rTMS and retraining in the treatment of focal hand dystonia. Front Hum Neurosci 2015;9:385.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Chen R, Wassermann EM, Caños M, Hallett M. Impaired inhibition in writer’s cramp during voluntary muscle activation. Neurology 1997;49:1054–1059.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Siebner HR, Filipovic SR, Rowe JB, Cordivari C, Gerschlager W, Rothwell JC, et al. Patients with focal arm dystonia have increased sensitivity to slow-frequency repetitive TMS of the dorsal premotor cortex. Brain 2003;126(Pt 12):2710–2725.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Benninger DH, Lomarev M, Lopez G, Pal N, Luckenbaugh DA, Hallett M. Transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of focal hand dystonia. Mov Disord 2011;26:1698–1702.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Buttkus F, Baur V, Jabusch HC, de la Cruz Gomez-Pellin M, Paulus W, Nitsche MA, et al. Single-session tDCS-supported retraining does not improve fine motor control in musician’s dystonia. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2011;29:85–90.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Buttkus F, Weidenmüller M, Schneider S, Jabusch HC, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, et al. Failure of cathodal direct current stimulation to improve fine motor control in musician’s dystonia. Mov Disord 2010;25:389–394.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Furuya S, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Altenmüller E. Surmounting retraining limits in musicians’ dystonia by transcranial stimulation. Ann Neurol 2014;75:700–707.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Bradnam LV, Graetz LJ, McDonnell MN, Ridding MC. Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation to the cerebellum improves handwriting and cyclic drawing kinematics in focal hand dystonia. Front Hum Neurosci 2015;9:286.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Sadnicka A, Hamada M, Bhatia KP, Rothwell JC, Edwards MJ. Cerebellar stimulation fails to modulate motor cortex plasticity in writing dystonia. Mov Disord 2014;29:1304–1307.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Rosset-Llobet J, Fàbregas-Molas S, Pascual-Leone Á. Effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on neurorehabilitation of task-specific dystonia: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Med Probl Perform Art 2015;30:178–184.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Opitz A, Paulus W, Will S, Antunes A, Thielscher A. Determinants of the electric field during transcranial direct current stimulation. Neuroimage 2015;109:140–150.ArticlePubMed
- 32. McDonald WM, Durkalski V, Ball ER, Holtzheimer PE, Pavlicova M, Lisanby SH, et al. Improving the antidepressant efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation: maximizing the number of stimulations and treatment location in treatment-resistant depression. Depress Anxiety 2011;28:973–980.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Dunner DL, Aaronson ST, Sackeim HA, Janicak PG, Carpenter LL, Boyadjis T, et al. A multisite, naturalistic, observational study of transcranial magnetic stimulation for patients with pharmacoresistant major depressive disorder: durability of benefit over a 1-year follow-up period. J Clin Psychiatry 2014;75:1394–1401.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Benabid AL, Cornu P, et al. Bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N Engl J Med 2005;352:459–467.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Kimberley TJ, Borich MR, Schmidt RL, Carey JR, Gillick B. Focal hand dystonia: individualized intervention with repeated application of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2015;96(4 Suppl):S122–S128.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Page SJ, Cunningham DA, Plow E, Blazak B. It takes two: noninvasive brain stimulation combined with neurorehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2015;96(4 Suppl):S89–S93.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Rosenkranz K, Butler K, Williamon A, Cordivari C, Lees AJ, Rothwell JC. Sensorimotor reorganization by proprioceptive training in musician’s dystonia and writer’s cramp. Neurology 2008;70:304–315.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Tinazzi M, Zarattini S, Valeriani M, Stanzani C, Moretto G, Smania N, et al. Effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on motor cortex excitability in writer’s cramp: neurophysiological and clinical correlations. Mov Disord 2006;21:1908–1913.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Hashimoto Y, Ota T, Mukaino M, Ushiba J. Treatment effectiveness of brain-computer interface training for patients with focal hand dystonia: a double-case study. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2013;2013:273–276.Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Transcranial magnetic stimulation: the road to clinical therapy for dystonia
Patrick J. Mulcahey, Angel V. Peterchev, Nicole Calakos, Noreen Bukhari-Parlakturk
Dystonia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Treatment of writer’s cramp based on current pathophysiological concepts
Kirsten E. Zeuner, Alexander Baumann, Karsten Witt
Dystonia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Technical Ability and Performing Scale (TAPS): A newly developed patient-reported functional rating scale for Musician's focal dystonia
Marina Ramella, Rosa Maria Converti, Giulia Giacobbi, Anna Castagna, Enrico Saibene, Francesca Borgnis, Francesca Baglio
Parkinsonism & Related Disorders.2022; 99: 79. CrossRef - Effects of non-invasive brain stimulation in dystonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jordan Morrison-Ham, Gillian M. Clark, Elizabeth G. Ellis, Andris Cerins, Juho Joutsa, Peter G. Enticott, Daniel T. Corp
Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders.2022; 15: 175628642211381. CrossRef - New modalities and directions for dystonia care
Genko Oyama, Nobutaka Hattori
Journal of Neural Transmission.2021; 128(4): 559. CrossRef - Taakspecifieke focale dystonie bij musici
T. DOOMS
Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Laryngeal Dystonia
Kristina Simonyan, Julie Barkmeier-Kraemer, Andrew Blitzer, Mark Hallett, John F. Houde, Teresa Jacobson Kimberley, Laurie J. Ozelius, Michael J. Pitman, Robert Mark Richardson, Nutan Sharma, Kristine Tanner, Gerald Berke, Tanya Eadie, Jeremy Greenlee, Mi
Neurology.2021; 96(21): 989. CrossRef - Treatment of focal hand dystonia: current status
Navnika Gupta, Sanjay Pandey
Neurological Sciences.2021; 42(9): 3561. CrossRef - Alterations of Interhemispheric Functional Connectivity and Degree Centrality in Cervical Dystonia: A Resting-State fMRI Study
Wenyan Jiang, Yiwu Lei, Jing Wei, Lu Yang, Shubao Wei, Qiong Yin, Shuguang Luo, Wenbin Guo
Neural Plasticity.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Update on current and emerging therapies for dystonia
Karlo J Lizarraga, Duha Al-Shorafat, Susan Fox
Neurodegenerative Disease Management.2019; 9(3): 135. CrossRef - Lasting Effects of Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Writer’s Cramp: A Case Report
Antonino Naro, Luana Billeri, Simona Portaro, Placido Bramanti, Rocco Salvatore Calabrò
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A unifying motor control framework for task-specific dystonia
Anna Sadnicka, Katja Kornysheva, John C. Rothwell, Mark J. Edwards
Nature Reviews Neurology.2018; 14(2): 116. CrossRef - Pain in focal dystonias – A focused review to address an important component of the disease
Micol Avenali, R. De Icco, M. Tinazzi, G. Defazio, L. Tronconi, G. Sandrini, C. Tassorelli
Parkinsonism & Related Disorders.2018; 54: 17. CrossRef - Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with Action Observation and Electromyographic Biofeedback Training in a Patient with Writer’s Cramp
Yohei Okada, Chiharu Shibamoto, Yukari Osumi, Chihiro Asano, Riho Takeuchi, Sachio Nabeshima, Shu Morioka, Koji Shomoto
Journal of Movement Disorders.2018; 11(2): 82. CrossRef - Dystonia
Bettina Balint, Niccolò E. Mencacci, Enza Maria Valente, Antonio Pisani, John Rothwell, Joseph Jankovic, Marie Vidailhet, Kailash P. Bhatia
Nature Reviews Disease Primers.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Stereotactic Lesioning of the Thalamic Vo Nucleus for the Treatment of Writer's Cramp (Focal Hand Dystonia)
Takeshi Shimizu, Tomoyuki Maruo, Shimpei Miura, Haruhiko Kishima, Yukitaka Ushio, Satoshi Goto
Frontiers in Neurology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Biased Visuospatial Attention in Cervical Dystonia
Gaetana Chillemi, Caterina Formica, Adriana Salatino, Alessandro Calamuneri, Paolo Girlanda, Francesca Morgante, Demetrio Milardi, Carmen Terranova, Alberto Cacciola, Angelo Quartarone, Raffaella Ricci
Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society.2018; 24(1): 22. CrossRef - Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)
Jean-Pascal Lefaucheur, Andrea Antal, Samar S. Ayache, David H. Benninger, Jérôme Brunelin, Filippo Cogiamanian, Maria Cotelli, Dirk De Ridder, Roberta Ferrucci, Berthold Langguth, Paola Marangolo, Veit Mylius, Michael A. Nitsche, Frank Padberg, Ulrich Pa
Clinical Neurophysiology.2017; 128(1): 56. CrossRef - Research Priorities in Limb and Task-Specific Dystonias
Sarah Pirio Richardson, Eckart Altenmüller, Katharine Alter, Ron L. Alterman, Robert Chen, Steven Frucht, Shinichi Furuya, Joseph Jankovic, H. A. Jinnah, Teresa J. Kimberley, Codrin Lungu, Joel S. Perlmutter, Cecília N. Prudente, Mark Hallett
Frontiers in Neurology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation as an Alternative Treatment in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease
Yeo Jin Kim
Brain & Neurorehabilitation.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Non‐invasive brain stimulation for dystonia: therapeutic implications
R. Erro, M. Tinazzi, F. Morgante, K. P. Bhatia
European Journal of Neurology.2017; 24(10): 1228. CrossRef - Cathodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Improves Focal Hand Dystonia in Musicians: A Two-Case Study
Sara Marceglia, Simona Mrakic-Sposta, Manuela Fumagalli, Roberta Ferrucci, Francesca Mameli, Maurizio Vergari, Sergio Barbieri, Alberto Priori
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
Comments on this article
 KMDS
KMDS
 E-submission
E-submission
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite